Cerebrovascular disease includes a range of conditions that affect the flow of blood through the brain. This alteration of blood flow can sometimes impair the brain’s functions on either a temporary or permanent basis. When such an event occurs suddenly, it’s referred to as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
Conditions that fall under the heading of cerebrovascular disease include:
Stroke: The most common type of cerebrovascular disease. The hallmark of a stroke is the permanent loss of sensation or motor function. The two general categories of strokes are hemorrhagic (bleeding into the brain) or ischemic (insufficient blood flow to the brain).
Transient ischemic attack (TIA): This is similar to a stroke, but the symptoms completely resolve within 24 hours. TIA is sometimes referred to as a “mini stroke.”
Aneurysms of blood vessels supplying the brain: An aneurysm is caused by a weakening of the artery wall, resulting in a bulge in the blood vessel.
Vascular malformations: This refers to abnormalities present in arteries or veins.
Vascular dementia: Cognitive impairment that is usually permanent.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: This term is used to describe blood leaking out of a blood vessel onto the brain’s surface.
Symptoms of cerebrovascular disease
The symptoms of cerebrovascular disease may differ slightly depending on the specific condition you have. However, stroke is the most common presentation of cerebrovascular diseases.
Strokes are characterized by sudden onset of symptoms, and survival and functional outcomes are time-sensitive. To help you identify the warning signs of a stroke, use the acronym FAST:
Facial droop: One side of the face may appear “droopy” or the person may be unable to smile.
Arm weakness: The person is unable to raise their arm above their head
Speech difficulty: The person has slurred speech, is unable to find words, or is unable to understand what people are saying to them
Time to call 911: Immediately seek medical attention if even one of these symptoms is present.
Other symptoms of a TIA or stroke include:
severe headache
vertigo or dizziness
vomiting and nausea
memory loss or confusion
numbness and tingling in the arm, leg, or face, usually on only one side of the body
slurred speech
vision problems
difficulty or inability to walk
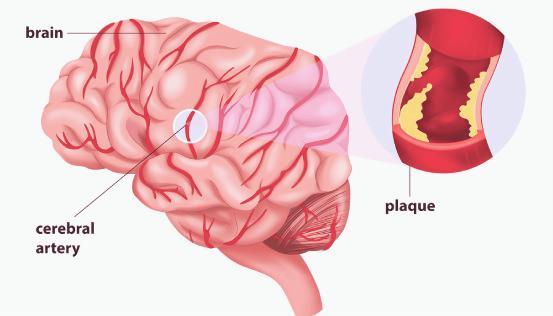
How it’s treated
The specific treatment depends on the type of cerebrovascular disease that you have. However, the treatment centers on improving your brain’s blood flow. Based on the cause of the loss of blood flow, your doctor will choose among several treatment options. The most effective treatment for you will depend on the extent of the loss of blood flow.
Most cases of cerebrovascular disease are treated with medications. These medications may include:
blood pressure medications
cholesterol medications
blood thinners
Medications are usually given to people whose arteries are less than 50 percent blocked or narrowed. In more severe cases, surgery to remove plaque or blockages, or to insert a stent may be required.
If brain function has already been reduced or altered by a cerebrovascular disease, then you may need to have physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy as a part of the recovery process.